Signs and Symptoms of Auditory Difficulties

Signs and Symptoms
It is essential for professionals and caregivers to be able to identify when somebody is having auditory processing difficulties. As well as sensory profiling people to identify their sensory difficulties, being able to recognise the signs of sensory needs is vital for effective management.
Auditory difficulties are common in individuals with Sensory Processing Difficulties (SPD).
Here are some signs of auditory difficulties specifically related to SPD:
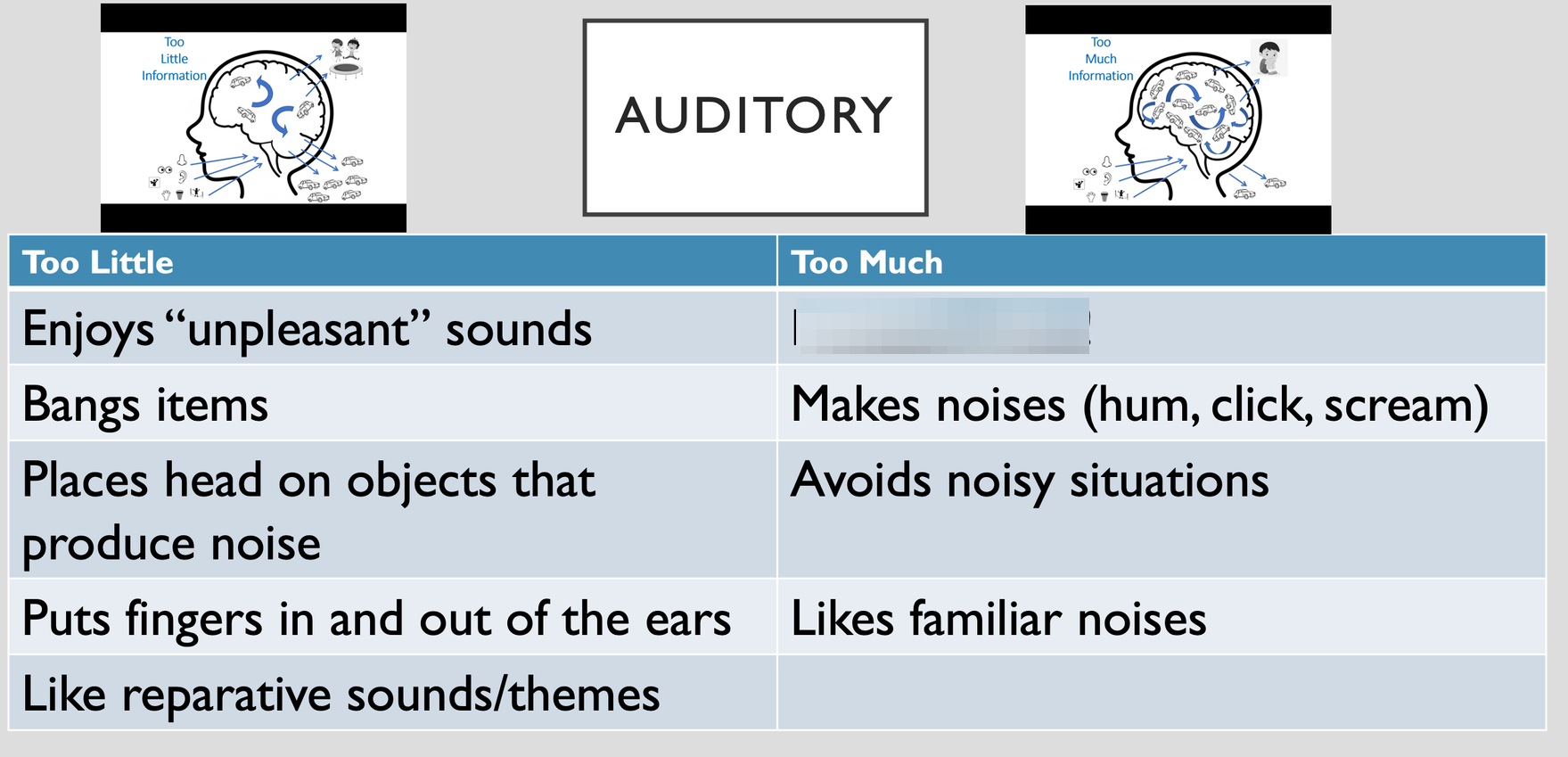
- Hypersensitivity to Sound: Individuals with SPD may be hypersensitive to certain sounds, experiencing them as overwhelming or painful. They may cover their ears or become distressed in response to everyday sounds such as loud voices, background noise, or sudden noises.
- Difficulty Filtering Background Noise: People with auditory difficulties related to SPD may have trouble filtering out irrelevant background noise, making it challenging to focus on important auditory information. They may struggle to concentrate in noisy environments, such as classrooms or crowded spaces.
- Overreaction to Loud Sounds: Individuals with SPD may exhibit exaggerated reactions to loud or unexpected noises. They may startle easily, become agitated, or display fight-or-flight responses in reaction to loud sounds that others perceive as normal or non-threatening.
- Delayed or Disorganised Language Development: Some individuals with SPD may experience delays or challenges in language development due to difficulties processing auditory information. They may have trouble understanding spoken language, following instructions, or expressing themselves verbally.
- Auditory Seeking Behaviors: In some cases, individuals with SPD may seek out intense auditory stimulation to regulate their sensory experiences. They may engage in behaviors such as making loud noises, tapping, or humming to satisfy their need for auditory input.
- Difficulty with Auditory Discrimination: SPD can affect an individual's ability to discriminate between different sounds or to recognize speech sounds accurately. They may have difficulty distinguishing between similar-sounding words, following conversations, or understanding speech in noisy environments.
- Auditory Fatigue: Processing auditory information can be mentally exhausting for individuals with SPD. They may experience auditory fatigue or cognitive overload after prolonged exposure to auditory stimuli, leading to decreased attention, concentration, or tolerance for further sensory input.
- Avoidance of Noisy Environments: People with SPD may actively avoid noisy or overstimulating environments to prevent sensory overload. They may prefer quiet, calm settings and may become anxious or distressed when exposed to excessive auditory stimuli.
- Difficulty with Social Communication: Auditory difficulties related to SPD can impact social communication skills. Individuals may struggle to engage in conversations, maintain eye contact, or interpret social cues due to challenges processing auditory information.
- Emotional and Behavioral Challenges: Auditory difficulties can contribute to emotional and behavioral challenges in individuals with SPD. They may experience frustration, anxiety, or sensory overload in response to auditory stimuli, leading to meltdowns, withdrawal, or other coping behaviors.
It's important to recognise that individuals with SPD may have unique sensory profiles and may experience auditory difficulties differently. Early identification and intervention, including sensory-based therapies and environmental modifications, can help individuals with SPD better regulate their sensory experiences and improve their quality of life. Working with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including occupational therapists, speech-language pathologists, and educators, can provide comprehensive support for individuals with auditory difficulties related to SPD.




